Breast Lift and Breast Augmentation



Save up to 70%
compared to UK prices
Internationally renowned
surgical team
Over 98% patient
satisfaction rate


Explore our competitive pricing for fat transfer breast augmentation in Turkey. Contact us for a personalised quote tailored to your needs.

breast surgery
in Turkey

breast augmentation

breast augmentation

breast augmentation
in Turkey
70% Cheaper Than the UK, the US, Canada and Ireland
Turkey’s Best Plastic Surgeons
English-Speaking Care & Thorough Post-Op Follow-Up
Ranked #1 in Turkey’s Medical Tourism

Fat transfer breast augmentation, also known as breast lipofilling, is gaining popularity in cosmetic surgery. This natural method uses the patient’s own fat to increase breast volume, offering an alternative to traditional implants. As surgical techniques evolve and demand for natural solutions grows, fat transfer breast augmentation is becoming a preferred choice for many women seeking to enhance their breast appearance.
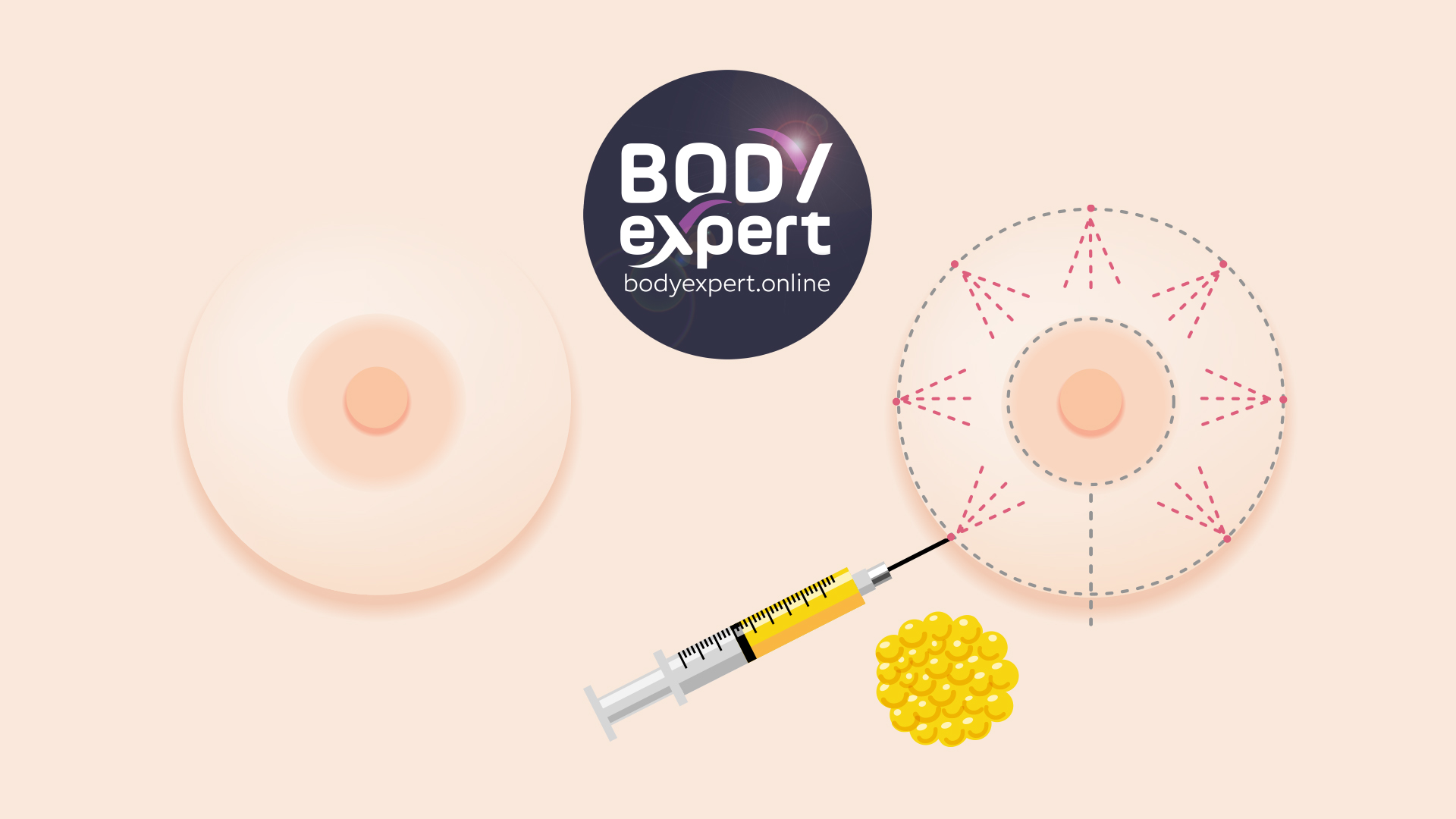
Fat transfer breast augmentation involves removing fat from one area of the patient’s body and injecting it into the breasts. This approach allows for a natural volume increase without using foreign materials.
The technique’s history dates back to 1893 when German surgeon Franz Neuber first used it to fill a facial scar. However, it was in the 1990s that Dr Sydney Coleman developed and popularised this technique for breast augmentation.
The growing interest in fat transfer breast augmentation can be attributed to increasing demand for natural solutions in cosmetic surgery, improved techniques for fat harvesting and injection, and more harmonious and natural results compared to implants.

Fat transfer breast augmentation involves three main stages: fat harvesting from an area with excess adipose tissue, purification and concentration of the harvested fat cells, and reinjection of the purified fat into the breasts to increase their volume.
The detailed process begins with gentle liposuction, where the surgeon uses fine cannulas to carefully aspirate fat from donor areas. The harvested fat is then centrifuged or decanted to remove excess fluids and debris, retaining only viable fat cells. Finally, the purified fat is injected into the breasts using micro-cannulas, creating multiple tunnels in different breast planes to optimise graft survival.

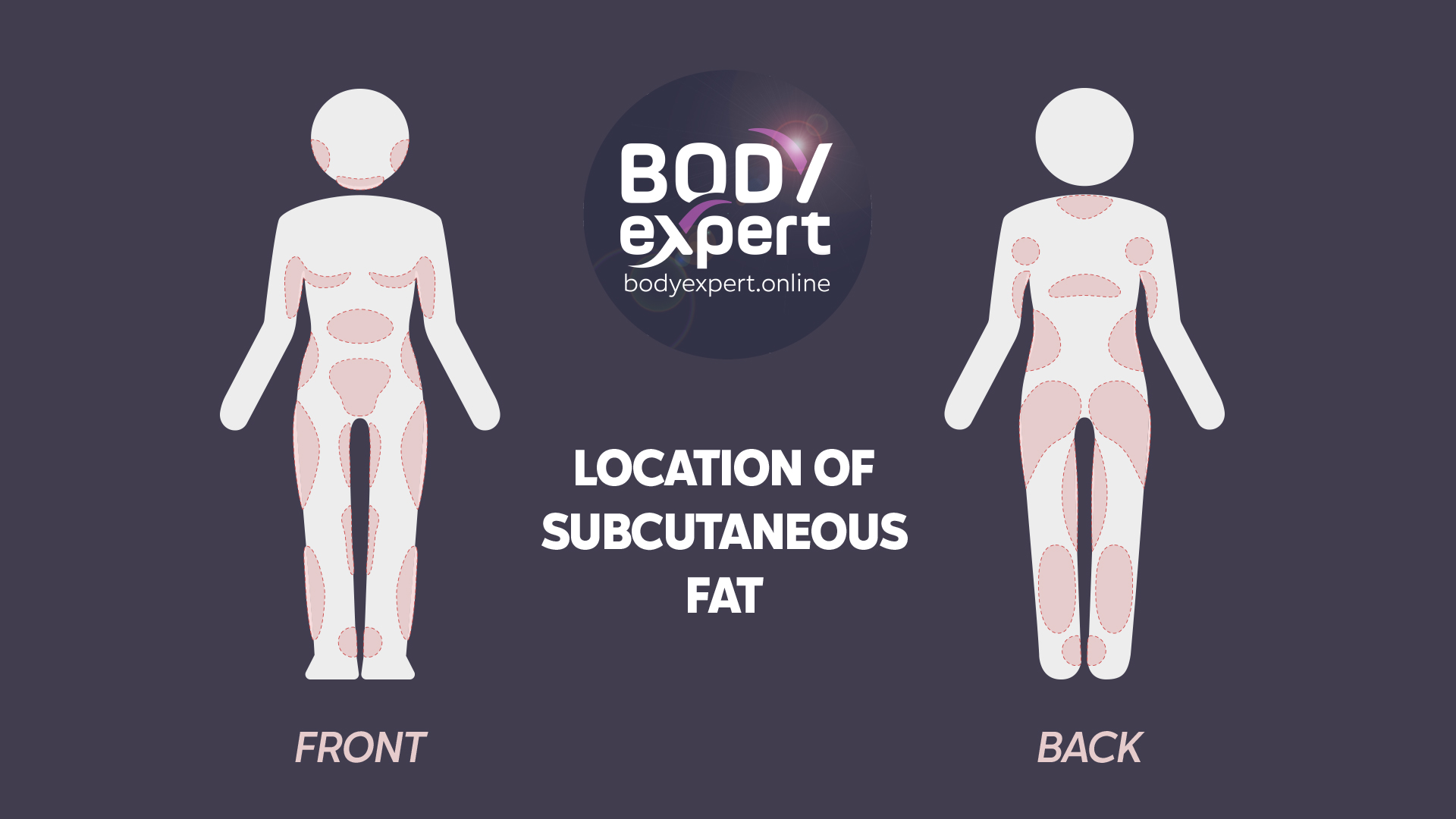
Common donor areas for fat transfer breast augmentation include the abdomen, hips and flanks, inner thighs, and inner knees. The choice of donor areas depends on the patient’s body type and is determined by the surgeon. One major advantage of fat transfer breast augmentation is the possibility of sculpting these areas simultaneously, offering dual aesthetic benefits in a single procedure.
Fat transfer breast augmentation is particularly suitable for moderate breast enlargement, correcting asymmetries, addressing irregularities after weight loss, pregnancy, or breastfeeding, and enhancing results after implant placement by softening contours for a more natural look.
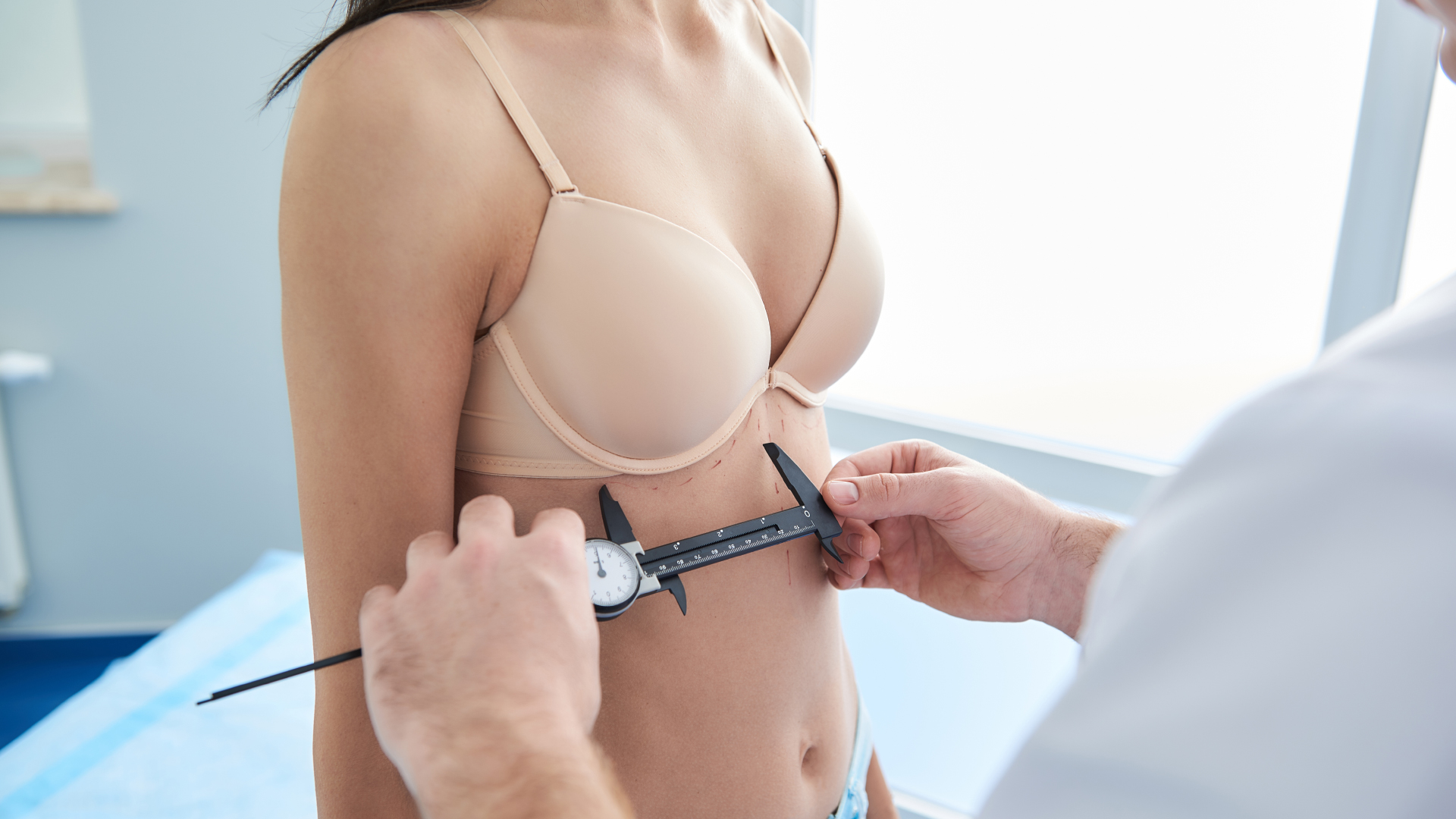
Before the procedure, a thorough consultation is essential. The surgeon performs a detailed clinical examination, assessing initial breast volume, skin quality and elasticity, and potential donor areas. The patient’s expectations are discussed, including desired volume and the potential need for multiple sessions.
The surgeon prescribes necessary examinations, such as a mammogram and/or breast ultrasound, and a preoperative blood test. These ensure there are no contraindications and allow for optimal procedure planning.
The type of anaesthesia is chosen based on the volume to be treated. Local anaesthesia with sedation may suffice for small volumes, while general anaesthesia is preferred for larger volumes. The procedure typically lasts 2 to 3 hours.
The process involves fat harvesting, where the surgeon infiltrates a tumescent solution into donor areas, then performs gentle liposuction using fine cannulas. The harvested fat is then processed through centrifugation or decantation to remove excess fluids and debris. Finally, the purified fat is precisely injected into the breasts using micro-cannulas, creating multiple tunnels in different breast planes.
After the procedure, patients can expect moderate pain, managed with painkillers, and bruising and swelling in harvesting and injection areas. They will need to wear a compression bra 24/7 for 1 month and should plan for a rest period of 2-3 days, with possible return to work after 3-7 days depending on activity.
Fat transfer breast augmentation offers a gradual and natural volume increase. Patients typically see about 50% of the result within the first month. Full results stabilise between 3 and 6 months post-procedure, allowing time for residual swelling to subside and surviving fat cells to integrate with surrounding tissues.
A key advantage of fat transfer is the natural look and feel of the breasts afterwards. The breasts remain soft, without the sensation of a foreign body often associated with implants. Moreover, fat transfer can improve breast skin quality, as stem cells in the transferred fat have a rejuvenating effect on skin elasticity and texture.
It’s important to note that a portion of injected fat cells doesn’t survive the transfer. This partial resorption occurs mainly in the first three months post-procedure. On average, 50 to 70% of injected fat survives and permanently integrates into breast tissues.
Factors influencing graft survival include surgical technique, smoking habits, pressure on the breasts post-operation, and significant weight fluctuations.
Typically, 2 to 3 fat transfer sessions are necessary for optimal results. These sessions are spaced 3 to 6 months apart, allowing complete tissue revascularisation between each session. This gradual approach enables progressive, natural breast volume increase and result refinement over time.
Fat transfer breast augmentation offers numerous benefits, including the use of the patient’s own tissues, natural-looking and feeling results, dual aesthetic benefit of breast enhancement and body contouring, minimal scarring, limited long-term risks compared to implants, possibility for fine-tuning breast asymmetries, and improvement in breast skin quality.
While generally safe, the procedure carries some risks, including general surgical risks like bleeding, haematomas, and infections, as well as specific risks such as significant fat resorption, oil cyst formation, calcifications, surface irregularities, and slight asymmetry.
Recovery after fat transfer breast augmentation is generally well-tolerated. Patients can usually resume light activities after 2-3 days and return to office work 3-7 days post-procedure. Gentle exercise can resume after 3-4 weeks, with intense activities resuming after 6-8 weeks.
Regular follow-up is crucial for monitoring healing and results. Consultations typically occur at 7-10 days, one month, three months, and six months post-procedure. Imaging examinations, including a 3-month ultrasound and a one-year reference mammogram, are also recommended.

In Turkey, the cost of fat transfer breast augmentation is typically more affordable than in Western European countries, ranging from €2,000 to €4,000 per session. The procedure is generally not covered by national health services for cosmetic purposes, though exceptions may exist for reconstructive needs. Private health insurance usually doesn’t cover this procedure unless deemed medically necessary.
Many patients consider medical tourism to Turkey for more affordable options. When choosing this route, it’s crucial to thoroughly research clinics and surgeons, considering factors beyond cost such as quality of care, safety standards, and post-operative follow-up.

Fat transfer breast augmentation represents a significant advancement in breast enhancement, offering a natural alternative to traditional implants. For those considering this procedure in Turkey, it’s essential to consult with experienced surgeons, understand the process thoroughly, and carefully weigh the benefits and risks before making a decision.

